Contact Lens Guide: Myopia, Astigmatism & Both Corrected
TL;DR: Contact lenses correct myopia (nearsightedness) by helping light focus directly on the retina instead of in front of it, while specialized toric contact lenses correct astigmatism by accommodating the eye’s irregular corneal shape with different powers across the lens. When you have both myopia and astigmatism together, toric contact lenses can simultaneously correct both refractive errors in a single lens, providing clear vision at all distances.
If you’re among the millions experiencing blurry vision from myopia, astigmatism, or both conditions together, you may be wondering how contact lenses can help restore clear sight. Modern contact lens technology has revolutionized the correction of these common refractive errors, offering solutions that weren’t available even a decade ago.
Whether you’re dealing with the distance blur of myopia, the all-distance distortion of astigmatism, or the complex combination of both conditions, today’s advanced contact lenses provide clearer, more comfortable vision than ever before. This comprehensive guide explores the science behind how contact lenses correct these vision problems, examines the latest treatment options, and helps you understand which solutions might be right for your specific needs.
The Science of Myopia Correction Through Contact Lenses
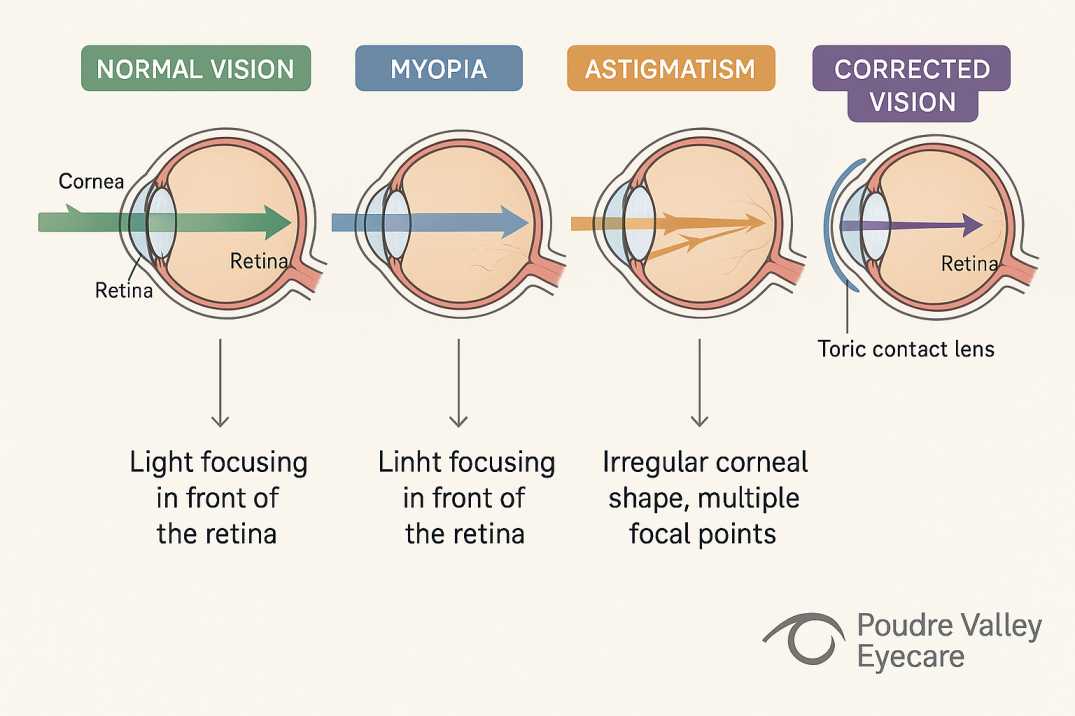
Myopia, commonly called nearsightedness, affects approximately 33% of Americans according to recent national health data, with rates having nearly doubled from 25% in the early 1970s to over 40% among younger populations by 2025. This refractive error occurs when the eye grows too long or the cornea curves too steeply, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it.
Clinical Presentation and Impact on Daily Function
Individuals with myopia typically demonstrate clear near vision capabilities—reading books or working on digital devices presents minimal difficulty. However, distant objects appear blurry and out of focus, manifesting as difficulty reading street signs, seeing presentation screens clearly, or experiencing reduced visual acuity during night driving due to blurred light sources.
The clinical severity of myopia ranges from mild cases (slight difficulty with distant object clarity) to high myopia (significant visual impairment that substantially increases the risk of serious ocular complications, including retinal detachment, glaucoma, and myopic macular degeneration). Understanding the degree of myopic progression helps determine the most appropriate contact lens intervention for each patient’s lifestyle and visual demands.
Optical Principles of Contact Lens Myopia Correction
Contact lenses correct myopia through precise optical manipulation of light rays entering the eye. Unlike spectacle lenses, which maintain a fixed distance of approximately 12 millimeters from the corneal apex, contact lenses rest directly on the precorneal tear film, creating a unified optical system that moves synchronously with ocular movement.
For myopia correction, contact lenses utilize negative (minus) diopter powers to create divergent light rays before they enter the eye’s optical system. This optical adjustment ensures that incoming parallel light rays achieve proper focal convergence directly on the retinal plane, thereby restoring sharp distance vision acuity essential for activities such as driving, sports participation, and professional presentations.
Key advantages of contact lenses over glasses for myopia:
- Unlimited peripheral vision without frame restrictions
- Natural field of view that moves with your eye movements
- No weather interference from rain, snow, or fogging
- Active lifestyle compatibility for sports and outdoor activities
- Aesthetic freedom from wearing frames
Evidence-Based Myopia Control Interventions
Contemporary research has demonstrated that specific contact lens designs can significantly decelerate the progression of myopia, particularly in pediatric and adolescent populations. These myopia control lenses function through peripheral defocus mechanisms, creating simultaneous focus on the central retina for clear vision while generating myopic defocus in the peripheral retina to inhibit axial eye growth.
Clinically validated myopia control options include:
MiSight 1-Day Lenses: FDA-approved daily disposable lenses featuring ActivControl Technology that has demonstrated a 52% reduction in axial elongation in randomized controlled trials spanning six years. These dual-focus lenses maintain central visual acuity while creating consistent peripheral myopic defocus that significantly slows myopia progression.
Center-Distance Multifocal Contact Lenses: Advanced multifocal designs utilizing center-distance optics, as validated in the BLINK (Bifocal Lenses in Nearsighted Kids) study, demonstrate substantial myopia control efficacy. The +2.50 Add power configuration has shown superior results with an average progression reduction of 46% compared to single-vision correction.
Orthokeratology (Ortho-K): Specialized overnight corneal reshaping lenses that create temporary central corneal flattening, providing unaided daytime vision while simultaneously reducing myopia progression by 40-60% through peripheral corneal steepening effects that create relative myopic defocus.
Advanced Astigmatism Correction: Toric Lens Technology and Applications
Astigmatism affects approximately 36% of Americans aged 20 and older, according to recent national survey data, representing one of the most prevalent refractive errors globally. This condition results from corneal or lenticular irregularities—instead of maintaining a perfectly spherical curvature similar to a basketball, the anterior corneal surface or crystalline lens exhibits an elliptical configuration resembling a football, with varying curvatures along different meridians.
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Considerations
Unlike myopia, which primarily affects distance visual acuity, astigmatism causes comprehensive visual disturbances across all focal distances. Patients typically present with:
- Distorted visual acuity at both near and distance ranges
- Asthenopic symptoms, including ocular fatigue and cephalgia, particularly following sustained near work
- Compromised scotopic vision with characteristic halo formation around light sources
- Compensatory squinting behaviors in attempts to achieve improved focus through pinhole effects
- General visual fatigue resulting from increased accommodative and convergence demands
Many individuals with mild astigmatism remain undiagnosed, attributing their intermittent visual discomfort to stress-related factors or occupational demands. However, even low-magnitude uncorrected astigmatism can significantly impact quality of life and overall visual performance metrics.
Toric Lens Design Principles and Stabilization Mechanisms
Conventional spherical contact lenses cannot adequately correct astigmatism due to their uniform curvature characteristics. Astigmatism requires toric contact lenses—sophisticated optical devices engineered with varying powers across different meridians to compensate for corneal or lenticular irregularities.
Advanced toric lens design features:
Differential Meridional Powers: Toric lenses incorporate two distinct curvature radii positioned perpendicular to each other, precisely matching the patient’s ocular elliptical configuration. One meridian corrects the steeper curvature while the orthogonal meridian addresses the flatter radius, ensuring optimal light convergence on the retinal plane.
Dynamic Stabilization Technology: Since toric lenses must maintain precise rotational orientation to provide optimal visual correction, they incorporate sophisticated stabilization mechanisms. Advanced systems, such as ACUVUE’s BLINK STABILIZED technology, utilize the natural blinking mechanism to continuously realign lens position, maintaining consistent visual acuity even during complex eye movements and head positioning changes.
Traditional Ballast Stabilization: Earlier toric lens designs employed inferior ballast weighting to maintain gravitational orientation, though this technology may experience positional instability during certain activities or specific body positions.
Contemporary Toric Lens Options and Clinical Applications
Daily Disposable Toric Lenses: Optimal for intermittent wear patterns, travel scenarios, or active lifestyle requirements. These lenses provide fresh, sterile optics daily with eliminated cleaning protocol requirements. Leading options include Clariti 1-Day Toric and ACUVUE OASYS 1-Day for Astigmatism, both offering superior comfort profiles and exceptional visual acuity.
Monthly Replacement Toric Lenses: Cost-effective solutions for consistent daily wear, featuring advanced biomaterials and moisture-retention technologies. Biofinity Toric and Air Optix for Astigmatism provide sustained all-day comfort with superior oxygen transmissibility for optimal corneal health maintenance.
Specialty Toric Configurations: For high-magnitude astigmatism or complex prescription parameters, custom-manufactured toric lenses can be produced to address specific refractive requirements, ensuring optimal visual correction where standard parameters prove insufficient.
Combined Refractive Error Management: Myopic Astigmatism Solutions
When patients present with both myopia and astigmatism—clinically termed myopic astigmatism—comprehensive optical correction requires contact lenses capable of addressing both refractive errors simultaneously. Advanced toric contact lenses can successfully incorporate negative spherical power for myopia correction alongside cylindrical power for astigmatism correction within a single optical device.
Clinical Assessment of Complex Refractive Errors
Myopic astigmatism represents a frequently encountered clinical presentation affecting millions of individuals globally. A typical prescription might indicate “-3.50 -1.25 x 180,” where:
- -3.50 D represents the spherical equivalent myopia correction requirement
- -1.25 D indicates the cylindrical power needed for astigmatism correction, n
- x 180° specifies the axis orientation for precise astigmatism correction
This combination results in patients experiencing both the distance visual blur characteristic of myopia and the multidirectional visual distortion typical of astigmatism, creating complex visual challenges requiring sophisticated optical intervention.
Advanced Optical Design for Complex Prescriptions
Contemporary toric contact lenses demonstrate exceptional capability in managing combined refractive errors simultaneously. These sophisticated optical devices integrate multiple power configurations across different meridians while maintaining the negative power characteristics essential for myopia correction.
Integrated correction mechanisms:
- Central optical zones provide the requisite negative diopter power to redirect myopic focus back to the retinal plane
- Meridional power variations correct astigmatic distortion by compensating for irregular corneal curvature patterns
- Advanced stabilization systems ensure maintained lens orientation for consistent, optimal visual acuity
Professional Fitting Protocols for Dual Correction
Successful toric lens fitting for myopia and astigmatism requires comprehensive clinical expertise and precision measurement techniques. The optimal fitting process includes:
Comprehensive corneal topography to determine precise ocular surface geometry and establish optimal lens parameters
Systematic trial fitting procedures utilizing multiple brands and designs to identify the optimal combination of visual acuity, comfort, and rotational stability
Precision refraction adjustments to achieve maximum visual acuity across all distance ranges
Structured follow-up protocols to ensure sustained clinical success and long-term ocular health
Specialized Contact Lens Modalities for Complex Cases
Beyond standard toric lenses, several advanced contact lens modalities provide superior visual outcomes for complex prescriptions or challenging clinical presentations:
Rigid Gas Permeable Lenses: Superior Optical Performance
RGP lenses maintain consistent shape characteristics on the ocular surface, creating a uniform optical interface that effectively masks corneal irregularities. For individuals with astigmatism, particularly moderate to high cylindrical corrections, RGP lenses frequently provide superior visual acuity compared to soft toric lenses.
Clinical advantages of RGP lenses:
- Exceptional visual acuity often exceeding soft lens optical performance
- Extended durability with typical annual replacement schedules
- Superior oxygen permeability supporting optimal long-term corneal physiology
- Enhanced correction capability for high-magnitude astigmatism
Clinical considerations: RGP lenses require a structured adaptation period of several weeks as patients adjust to the firmer lens material. However, most individuals find the superior visual quality justifies the initial accommodation period.
Scleral Lenses: Advanced Technology for Complex Corrections
Scleral lenses vault completely over the corneal surface, establishing contact exclusively with the conjunctival sclera. These larger-diameter lenses create a fluid-filled reservoir between the lens posterior surface and corneal epithelium, providing exceptional comfort and visual quality for challenging refractive cases.
Primary clinical indications:
- High-magnitude astigmatism exceeding standard toric lens parameter availability
- Irregular astigmatism secondary to corneal ectasia, keratoconus, or post-surgical changes
- Post-keratoplasty patients with corneal scarring or surface irregularities
- Severe dry eye syndrome patients who benefit from continuous corneal hydration
Hybrid Lens Technology: Integrated Optical Solutions
Hybrid contact lenses feature a central rigid gas-permeable zone for optimal optics surrounded by a soft hydrogel periphery for enhanced comfort. This innovative design delivers the exceptional visual acuity characteristic of RGP lenses while providing improved comfort profiles and reduced displacement risk.
Current Clinical Research and Evidence-Based
Study 1: Six-Year MiSight Clinical Trial Outcomes (2022-2024)
The comprehensive MiSight study, with results published in Optometry and Vision Science through 2024, represents the longest prospective evaluation of children wearing dual-focus contact lenses for myopia control. This landmark research demonstrated sustained myopia control with a 52% reduction in axial eye growth compared to single-vision lenses over six years.
Notably, children who transitioned from single-vision control lenses to MiSight lenses after the initial three-year period experienced a 71% reduction in axial elongation during their subsequent three-year treatment period, providing compelling evidence for the efficacy of initiating myopia control interventions at any developmental stage.
Clinical significance:
- No rebound effect observed with continued treatment
- Excellent safety profile with no serious adverse events reported
- Sustained efficacy demonstrated over extended follow-up periods
- Strong evidence supporting early intervention benefits
Study 2: BLINK Study Long-Term Clinical Outcomes (2023-2025)
The Bifocal Lenses In Nearsighted Kids (BLINK) study evaluated multifocal contact lenses across extended timeframes, with recent publications in JAMA Ophthalmology demonstrating continued clinical benefits through 2025. Children utilizing +2.50 Add multifocal lenses demonstrated a 46% reduction in myopia progression with maintained accommodation function following 4.7 years of lens wear.
Research implications:
- Confirmed long-term safety of multifocal lens wear in pediatric populations
- No adverse impact on normal accommodation development processes
- Established +2.50 Add as optimal power for myopia control efficacy
- Demonstrated clinical feasibility of initiating myopia control in school-age children
Study 3: Advanced Spectacle Lens versus Contact Lens Efficacy Comparison (2025)
Recent comparative research published in the American Journal of Ophthalmology evaluated highly aspherical lenslet spectacles versus contact lens interventions over three years. While both modalities demonstrated myopia control benefits, contact lenses exhibited superior peripheral defocus profiles due to their synchronized movement with ocular rotation, supporting their position as gold-standard myopia control interventions. Research implications:
- Contact lenses provide more consistent peripheral defocus profiles
- Natural ocular movement compatibility gives contacts advantages over spectacle corrections
- Supports contact lenses as first-line myopia control interventions
- Validates the critical importance of proper lens fitting for optimal clinical outcomes
Economic Considerations and Healthcare Access
Contemporary Cost Analysis for Contact Lens Correction
Daily disposable toric lenses: $600-900 annually (approximately $50-75 per month for bilateral correction)
Monthly replacement toric lenses: $300-650 annually, including cleaning solutions and storage case replacements
Specialty lens modalities (RGP, scleral, hybrid): $800-1,500 initial investment with reduced annual replacement costs
Vision insurance coverage: Most vision plans provide annual contact lens allowances ranging from $150-300, with comprehensive plans offering up to $400, substantially reducing patient out-of-pocket expenses
Value-Based Healthcare Considerations
When evaluating contact lens investments, patients should consider comprehensive benefits, including:
- Lifestyle enhancement through sports participation capabilities and aesthetic preferences
- Professional advantages from unrestricted peripheral vision in occupational settings
- Long-term ocular health through proper refractive correction and myopia control interventions
- Quality of life improvements from consistent, reliable visual acuity
Patient Selection Criteria and Clinical Decision-Making
Comprehensive Assessment Factors
Lifestyle and occupational requirements:
- Active individuals and athletes often benefit from daily disposable options
- Budget-conscious patients may prefer monthly replacement schedules
- Professional environments requiring extensive visual fields favor contact lens correction
- Pediatric populations often demonstrate excellent compliance with daily disposables for hygiene optimization
Prescription complexity considerations:
- Simple myopia correction: Multiple lens options are typically available
- Low-magnitude astigmatism: Soft toric lenses usually provide adequate correction
- High-magnitude astigmatism: May require RGP or scleral lens modalities
- Combined refractive errors: Toric lenses with integrated myopia correction
Ocular health and physiological factors:
- Dry eye syndrome: Daily disposables or scleral lenses may be optimal
- Allergic conjunctivitis: Daily disposables minimize allergen accumulation
- Post-surgical corneas: May require specialty lens designs
- Age-related changes: Regular monitoring and prescription modifications are essential
Future Directions in Contact Lens Technology
Emerging Innovations and Research Developments
Smart contact lens technology incorporating glucose monitoring capabilities represents a significant advancement in healthcare monitoring through ocular interfaces, with potential applications extending beyond diabetes management.
Advanced myopia control designs continue evolving with sophisticated optical profiles and next-generation materials optimized for long-term ocular health and enhanced myopia progression control.
Novel biocompatible materials featuring enhanced oxygen transmissibility and superior moisture retention characteristics promise improved comfort profiles for extended wear applications.
Precision customization technology enables increasingly sophisticated lens manufacturing tailored to individual corneal topography and complex prescription requirements, approaching true personalized vision correction.
Additional Resources and Research Citations
For those seeking to explore the scientific research and professional resources that inform modern contact lens correction and myopia control, we recommend these authoritative sources:
Professional Research and Clinical Studies
1. Myopia Management 2025 – Contact Lens Spectrum
Comprehensive review of current myopia control interventions and latest clinical trial results
https://www.clspectrum.com/issues/2025/march/myopia-management-2025/
This peer-reviewed publication provides the most current evidence-based analysis of myopia management strategies, including detailed results from the MiSight 6-year study and BLINK trial outcomes that inform contemporary recommendations for contact lens myopia control interventions.
2. Long-term Effect of Dual-focus Contact Lenses – Optometry and Vision Science
Six-year multicenter clinical trial demonstrating sustained myopia control benefits
https://journals.lww.com/optvissci/fulltext/2022/03000/long_term_effect_of_dual_focus_contact_lenses_on.2.aspx
This landmark study, published in the leading optometry research journal, provides the scientific foundation for understanding how dual-focus contact lenses achieve sustained myopia control, supporting clinical discussions of treatment efficacy and safety profiles.
3. Understanding Myopia and Its Prevalence – National Academies of Sciences
Comprehensive analysis of myopia causes, prevention, and treatment strategies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK607610/
Published by the National Academy of Medicine, this authoritative resource establishes current myopia prevalence statistics and epidemiological trends that inform our understanding of the growing need for effective vision correction solutions, including contact lens interventions.
These resources represent the gold standard in contemporary eye care research and provide the scientific foundation for the treatment recommendations and statistical information presented throughout this clinical guide.
Clinical Practice Integration and Patient Care
The decision between contact lenses and spectacle correction, or selection among various contact lens modalities, requires comprehensive clinical assessment and collaborative patient decision-making. Optimal outcomes depend on a thorough evaluation of lifestyle factors, visual requirements, and individual preferences to recommend the most appropriate correction strategy.
Contemporary clinical practice emphasizes comprehensive eye examinations, advanced corneal topography when indicated, and systematic trial fitting procedures to ensure optimal visual acuity and comfort. Access to the complete spectrum of contact lens technologies and designs ensures patients receive the most appropriate correction for their unique clinical presentation.
The path to optimal visual correction extends beyond initial successful contact lens fitting. Structured follow-up care, proper lens hygiene protocols, and ongoing communication regarding any changes in vision or comfort help ensure sustained clinical success and long-term ocular health.
Whether initiating contact lens wear or considering upgrades from current correction modalities, today’s advanced lens technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for clear, comfortable vision. With appropriate professional guidance and commitment to proper lens care protocols, contact lenses can provide the visual freedom and lifestyle benefits essential for modern living.
Optimal vision outcomes result from understanding available options and collaborating with experienced eye care professionals who prioritize ocular health and visual success. Professional consultation can explore how modern contact lens technology can enhance vision and improve the quality of life.
Note: All pricing information, statistics, and research data in this article have been verified against current 2025 sources and reflect the most recent available information. Individual costs may vary based on prescription complexity, geographic location, and insurance coverage. This information is provided for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice.
FAQs
-
Contact lenses correct myopia by focusing light directly on the retina. They bend incoming light rays to compensate for the elongated eye shape, providing clear distance vision.
Please note: None of the above should be considered medical advice. If you’re having any concerns about your vision, please reach out to us immediately or see your primary care provider.